In a world where digital transformation defines competitiveness, managing information efficiently is no longer optional—it’s a strategic imperative. Modern businesses, especially those in tax, finance, legal, accounting, and real estate, handle thousands of documents daily. That’s where Optical Character Recognition (OCR) steps in, turning document overload into streamlined intelligence.
By integrating OCR into document management systems, organizations can bridge the gap between paper-based processes and AI-powered automation — a shift that simplifies operations, boosts accuracy, and unlocks measurable business value.
What Is OCR and How Does It Work?
OCR, short for Optical Character Recognition, is a technology that converts printed or handwritten text into machine-readable data. Using advanced algorithms and AI models, OCR systems scan and interpret characters from images, PDFs, or scanned documents, transforming them into searchable, editable digital content.
Modern OCR systems go beyond simple text extraction. They use AI-powered pattern recognition and machine learning (ML) to detect layout, font, and even handwriting nuances, ensuring higher accuracy across complex document structures.
Modern Document AI/IDP can detect layout (tables, headers, form fields), extract relationships, and integrate with RPA for end-to-end automation.
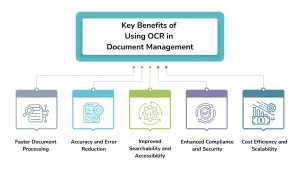
Key Benefits of Using OCR in Document Management
Document management is the backbone of operational efficiency. When combined with OCR, it evolves from basic storage to intelligent data processing. Here are the top benefits businesses realize:
1. Faster Document Processing
By automating data capture, OCR eliminates the need for manual input tasks. What once took hours of typing or verification now happens far more quickly. This accelerates processes like client onboarding, tax preparation, and contract validation.
2. Accuracy and Error Reduction
Manual document entry invites human error. OCR-driven automation ensures consistently accurate data extraction, reducing rework and data discrepancies, which are critical for finance- and compliance-focused industries.
3. Improved Searchability and Accessibility
Documents processed through OCR are transformed into indexed, searchable files. Teams can instantly retrieve client records or invoices using a simple keyword search instead of sorting through folders or emails.
4. Enhanced Compliance and Security
OCR systems integrated into enterprise document platforms provide audit trails, access controls, versioning, and assisted PII redaction. With the right configuration, they can support privacy obligations (e.g., HIPAA/GDPR) and financial recordkeeping rules (e.g., SEC Rule 17a-4/FINRA). Note that platform-level controls and organizational processes ultimately ensure compliance.
5. Cost Efficiency and Scalability
By reducing manual workloads and errors, businesses can cut down operational costs while scaling effortlessly as data volumes grow. OCR allows organizations to handle large data inflows without increasing resource dependency.
OCR Use Cases Across Industries
Financial Services & Accounting
OCR transforms invoice processing by automatically extracting vendor names, line items, amounts, and tax details from scanned or digital invoices. This automation minimizes errors, speeds up accounts payable, and validates extracted data against purchase orders for accuracy, keeping records audit-ready and compliant with tax laws.
Legal
Law firms use OCR to digitize case files, contracts, and legal briefs. This enables instant keyword searches across large document sets, accelerates case preparation, and ensures sensitive documents are stored securely, searchable, and compliant with retention policies.
Tax Resolution
OCR helps tax professionals swiftly process client forms and supporting documents. By extracting relevant data from various document types, OCR reduces manual entry errors, streamlines error checking, and eases compliance across complex, high-volume client portfolios.
Real Estate
Agencies and property managers automate the intake of property records, lease agreements, and mortgage documents with OCR. Fast data capture, automated indexing, and rapid retrieval help close deals faster and maintain complete digital archives.
Logistics
OCR processes shipping documents, bills of lading, and delivery receipts to extract order details into logistics systems. This results in traceable, real-time updates, reduced processing delays, and improved data for supply chain analytics.
The Future of OCR: Smarter, Context-Aware, and AI-Driven
OCR is no longer limited to text extraction; it’s evolving into a comprehension engine powered by artificial intelligence, multimodal processing, and contextual understanding.
The next generation of OCR is not just digitizing documents but interpreting them just like humans would, with accuracy, learning capability, and context awareness.
1. Intelligent Character Recognition (ICR)
ICR systems now apply deep learning with self-supervised pretraining, allowing them to understand various languages and file formats. By learning from unlabeled data, ICR improves accuracy across handwritten forms (clear handwriting; free-form cursive/mixed notes often need human-in-the-loop review), regional scripts, thus reducing the need for frequent manual retraining.
2. Context-Aware Data Understanding
Modern OCR has transformed into Smart OCR, capable of understanding the meaning and layout of content. It identifies document structures like tables, headers, and form fields — extracting not just text, but relationships between data points.
3. Integration with Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and RPA
OCR now functions as a crucial component of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) — combining AI, NLP, and Robotic Process Automation to deliver end-to-end automation. Integrated systems can now analyze visual and textual data simultaneously using vision-language models, generating summaries, extracting insights, and validating data automatically.
4. Cloud and Mobile-First Document Management
Cloud adoption continues to accelerate OCR scalability. Cloud-based OCR systems enable teams to scan and process documents anywhere, offering global accessibility, instant synchronization, and powerful collaboration features. Paired with mobile-first interfaces, OCR-equipped apps now allow employees to capture and process documents securely in the field — an essential advantage in hybrid and global operations.
5. Multimodal and Generative OCR
The next generation of OCR systems will be multimodal, capable of interpreting text, images, and even voice annotations together. Using generative AI, these models improve incomplete or low-quality documents, enabling enhanced intelligent search and analytics functions across document repositories.
Transform Your Operations with Smarter Document Management
Organizations that harness OCR today aren’t just automating workflows—they’re building resilient, intelligent enterprises ready to thrive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
The shift from paper-based processes to fully digital, AI-driven workflows isn’t just a trend; it’s the new standard for industry leadership and lasting innovation.
At Nablasol, we empower your organization to stay ahead by unifying fragmented data, automating complex workflows, and unlocking actionable insights—so you can deliver results faster, with unmatched accuracy and agility.
Connect with Nablasol to discover how our intelligent document management solutions, powered by OCR, can transform your operations and give you a decisive edge.
FAQs
Can OCR detect handwriting?
Yes, but only to a certain extent. Traditional OCR works best with printed text, while ICR (Intelligent Character Recognition) — an advanced form of OCR — can accurately read and interpret handwritten text using AI and machine learning. Modern OCR systems combining ICR and NLP now achieve high accuracy. Free-form cursive and mixed notes remain challenging, so confidence thresholds and human review are recommended.
What are the challenges of OCR?
Despite major advancements, OCR still faces challenges such as:
- Poor image quality or low-resolution scans that reduce accuracy.
- Complex layouts with tables, mixed fonts, or multi-column text.
- Handwritten or cursive text that standard OCR struggles to interpret.
- Language and script variations require specialized models.
- Data security and compliance when processing sensitive documents.
These limitations can be minimized by using AI-driven OCR and ICR solutions with proper preprocessing and integration into secure document management systems.
What is the difference between OCR, ICR (Intelligent Character Recognition), and IDP (Intelligent Document Processing)?
- OCR: Basic text extraction from images/scans.
- ICR: Built upon OCR, capable of handling handwritten text, different scripts, and more variable formats (often using deep learning).
- IDP: A broader system that includes OCR/ICR for text extraction, plus AI/NLP for classification, context understanding, workflow integration, and automated decision-making.
How accurate is OCR technology?
OCR accuracy depends on several factors: image quality (resolution, clarity, skew), document layout complexity, font types/handwriting, language/script, and preprocessing (noise removal).Modern OCR plus AI/ML enhancements (layout detection, training on handwritten text) improve accuracy, but there is still no “100% correct” guarantee — especially for poor-quality scans or highly complex documents.